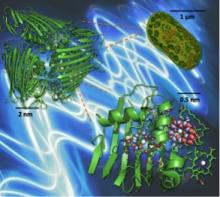
Dr Alex Chin and Dr Tim Zuehlsdorff (TCM), Dr Daniel Cole (Newcastle University) and Dr Nicholas Hine (University of Warwick)
The high efficiency of photosynthetic light reactions has been studied for many decades, revealing the critical role of optimised, purpose-built biological nanostructures, known as pigment-protein complexes (PPCs), in directing solar energy transport. The underlying physics of this versatile class of “devices” are still not fully understood, yet the recent and unexpected discovery that PPCs can support robust quantum (“wave-like”) dynamics has brought forth the exciting idea that the answers may lie within a full quantum mechanical theory of PPCs.
This project aims to develop the computational tools to provide such a description, enabling us to pinpoint the role of quantum effects in natural PPCs and also how such normally fragile effects are shielded from the noisy biological environment. Specifically, we will use new advances in linear-scaling quantum mechanical simulations to elucidate the origin of coherent, delocalised excited states of the Fenna-Matthews-Olson complex in unprecedented detail. The properties of these states, including how they change under the thermal deformations of the protein structure, will be analysed and used to simulate real-time, ultrafast (fs-ps) quantum dynamics, providing novel insight into the hierarchy and interconnections between structure, electronic properties and functional dynamics which are uniquely exploited in PPCs. These intricate functional relations will also be explored in another important, though less widely explored context: the structural reaction pathways of the oxygen-evolving complex that catalyses photosynthetic water splitting in higher plants.