Submitted by Dr Nalin Patel on Wed, 30/04/2014 - 11:13
Research in the solar energy community has always looked to natural photosynthetic systems for inspiration. The study of hybrid systems, made up of natural biological systems and synthetic materials is interesting both as a basis for “proof of principle” device fabrication, but more importantly serves as a platform for further fundamental research into the mechanisms of photosynthesis. Fusion of biological materials with synthetic systems has opened up new lines of experimentation, such as protein-film electrochemistry, which allow us to probe deeper into the underlying photochemistry and biophysics of the systems. The central aim of such research is to unravel new concepts, or further explain old ones in order to enhance our “pool of knowledge” in order to assist the development of next generation artificial photovoltaics and solar fuel cells.
The group of Dr Erwin Reisner was invited to write a tutorial view centred on such work. The team led by Dr Reisner consisted of ex-group member Dr Masaru Kato (Assistant Professor, Hokkaido University, Japan) and current members Dr Jenny Z. Zhang (Marie Curie Fellow, University of Cambridge, UK) and Nicholas Paul (Winton Scholar, University of Cambridge, UK). It describes current progress towards the design and study of photosystem II water oxidation enzymes incorporated into various synthetic electrode systems. The review also makes reference to other aspects of protein-film (photo-)electrochemistry. The review can be divided into three easy to follow sections:
1) Description of the basic structure, enzymatic function and photophysics of photosystem II proteins
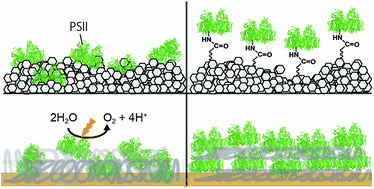
2) Protein-film photoelectrochemistry: the technique, it’s applications, use with PSII, and studying electron transfer mechanisms
3) Bio-inspired synthetic water oxidation systems. Artificial systems designed for the oxidation side of solar fuels production, which have been inspired by PSII are described in detail
This review should serve as both a short update on the most recent progress relevant for researchers currently studying within the field, and as an easy to follow introductory to the field for non-specialists and new graduate students coming into the world of bio-inspired solar energy research.
The review is featured in Chemical Society Reviews (Royal Society of Chemistry, UK).